Here is guide how you can easily deploy nginx web server on minikube locally with common kubernetes terms explaied as well in the tutorial.
Nginx Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: my-nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx-deployment
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx-deployment
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
resources:
limits:
cpu: "500m" # 500 milliCPU (0.5 CPU)
memory: "512Mi" # 512 Mebibytes
requests:
cpu: "200m" # 200 milliCPU (0.2 CPU)
memory: "256Mi" # 256 Mebibytes
Note - we have to use apps/v1 for Deployment and metadata is very important. The name nginx-deployment in metadata refers to name of deployment.
This name must match with selector -> matchLabels -> app name. The spec means specification of the deployment. T
If selector matchlabels do not match template labels, it gives error.
Properly add tabs at each line as bad spaces lead to misconfigurations and errors.
NodePort code to expose 80 port of nginx to outside
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment-nodeport
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: nginx-deployment
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8080
targetPort: 80
Here targetPort is port on pods targeted by service and port is the port of service exposed.
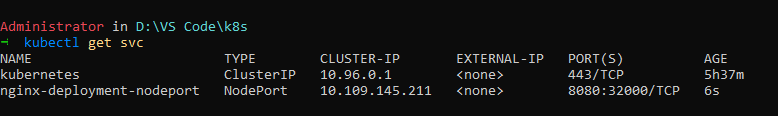
Note - Type minikube ip in terminal and then curl http://<minikube_ip>:<port_number> to see the response.
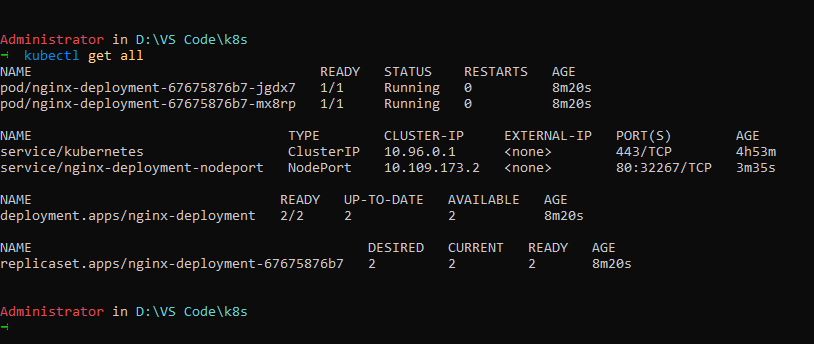
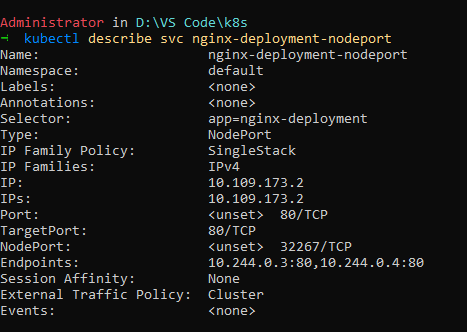
This port 80 of deployment is mapped to 32267 of minikube and can be accessed via minikube ip.
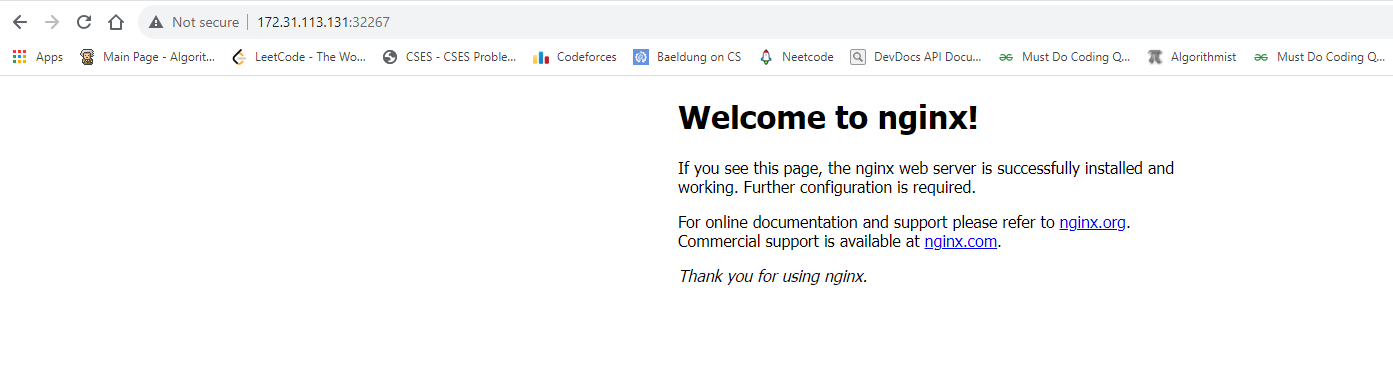
Note -
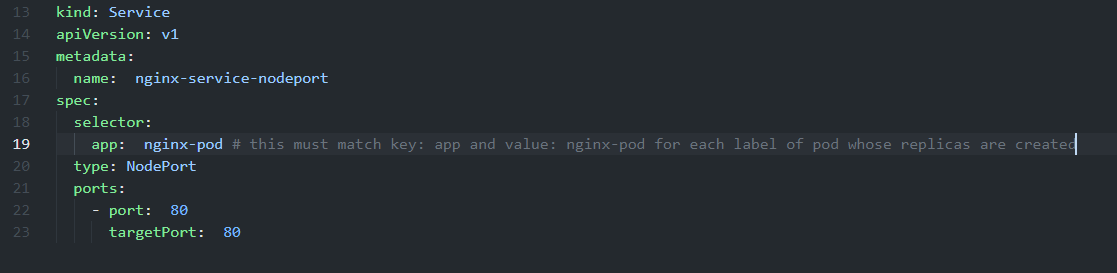
In order to check do kubectl get svc and check the endpoints of service to confirm if pods are connected to it or not.
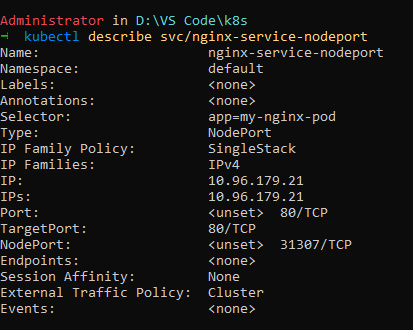
if endpoints is none, it means service is not connected to the pods.
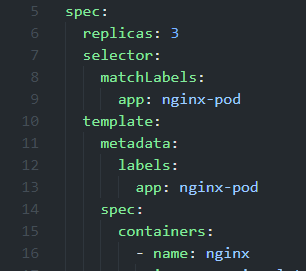
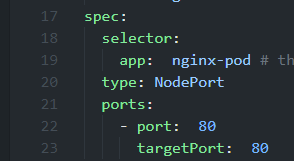
It is important that the selector.matchLabels.keyName matches the metadata.labels.keyName and here keyName is app. And this app: nginx-pod must match selector.keyName of the service.
Editing Deployments
You can edit existing deployments by kubectl edit deployment/my-nginx-deployment and this opens the current yaml file.
If things are changed then it creates another deployment to replace the existing and once done, it sets the running pods to 0 of old deployment and uses the edited yaml as the new deployment.
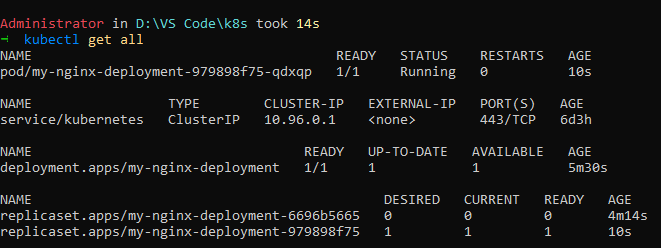
Here the pods are set to 0 of the replicaset created declaratively via deployment.
Use kubectl describe to see the changes being visible.
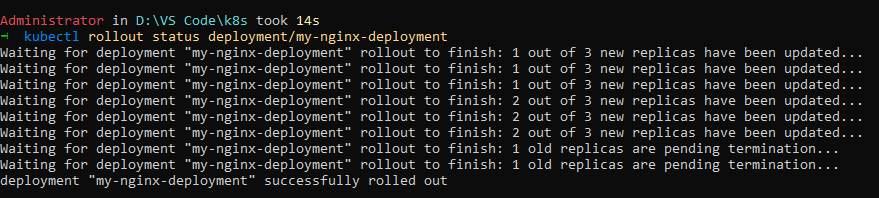
After editing, rollout changes are being made. kubectl rollout status deployment/nginx-deployment to see the status.
kubectl describe deployments gives the result -
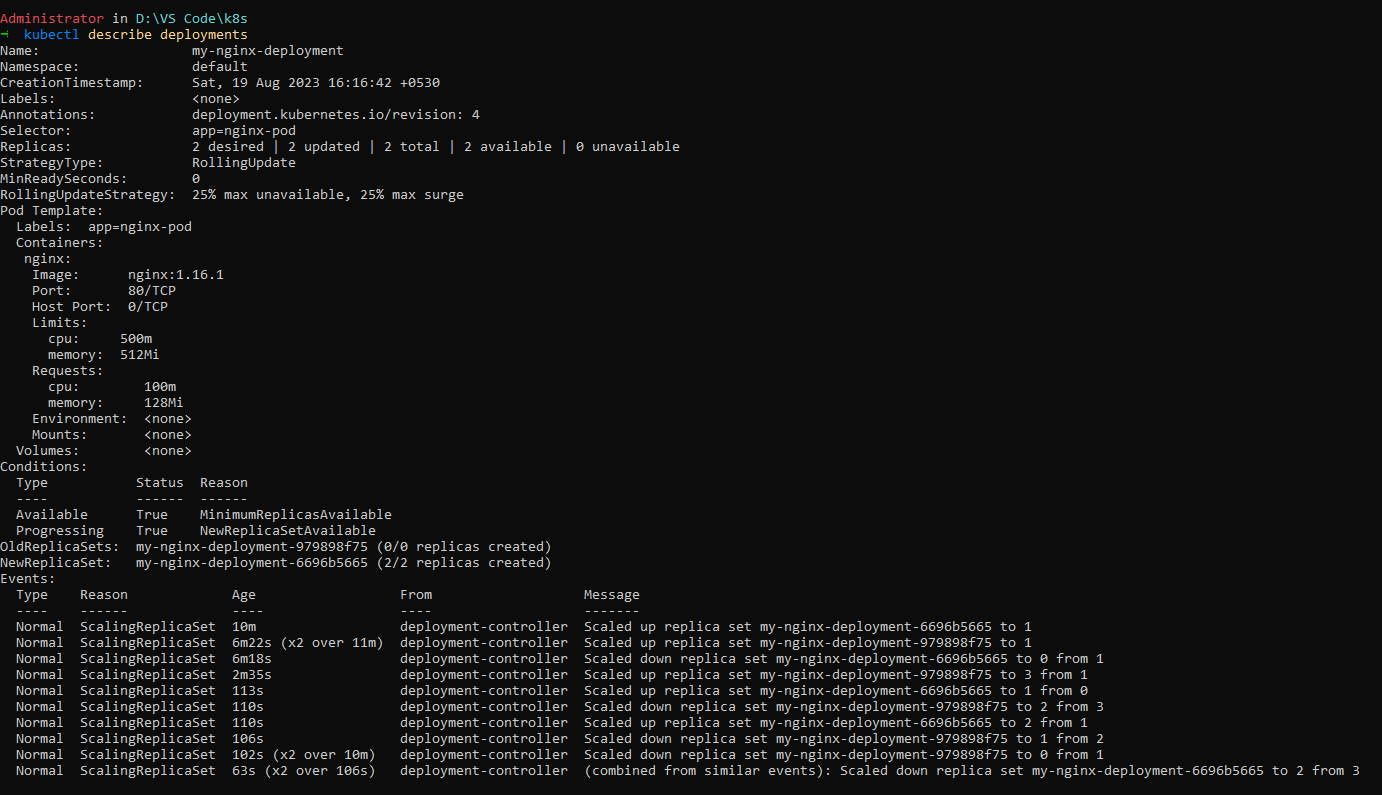 please open above image in new tab
please open above image in new tab
Note -
- If you update a Deployment while an existing rollout is in progress, the Deployment creates a new ReplicaSet as per the update and start scaling that up, and rolls over the ReplicaSet that it was scaling up previously – it will add it to its list of old ReplicaSets and start scaling it down.
- In API version apps/v1, a Deployment’s label selector is immutable after it gets created. It is better to decide your selectors before hand.
Rollback Deployments
kubectl rollout history deployment/nginx-deployment use this command to check the rollback history.
Output -
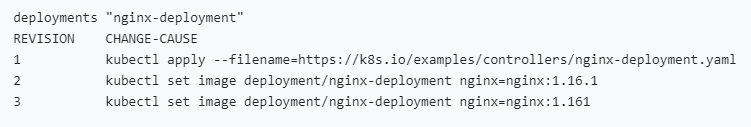
To get details of each revision, do kubectl rollout history deployment/nginx-deployment --revision=2
To rollback to a previous version
kubectl rollback undo deployment/nginx-deployment - this will rollback to just previous deployment.
kubectl rollout undo deployment/nginx-deployment --to-revision=2 - this will rollback to revision number 2 as the specific version.
Scaling deployments
kubectl scale deployment/nginx-deployment --replicas=10